Have you ever felt tired, achy, stressed, or unable to sleep—and couldn’t figure out why? Many people experience these symptoms daily without realizing that a simple mineral deficiency could be the reason.
Magnesium is one of those nutrients most people don’t think about until something feels “off.” Yet, it quietly supports hundreds of processes inside your body every single day.
From muscle movement to brain function and heart health, magnesium plays a much bigger role than most people realize.
Understanding what magnesium does for the body can help you feel stronger, calmer, more energized, and healthier overall—naturally.
Quick answer:
Magnesium is an essential mineral that helps your muscles move, nerves function, heart stay steady, bones stay strong, and energy levels stay balanced.
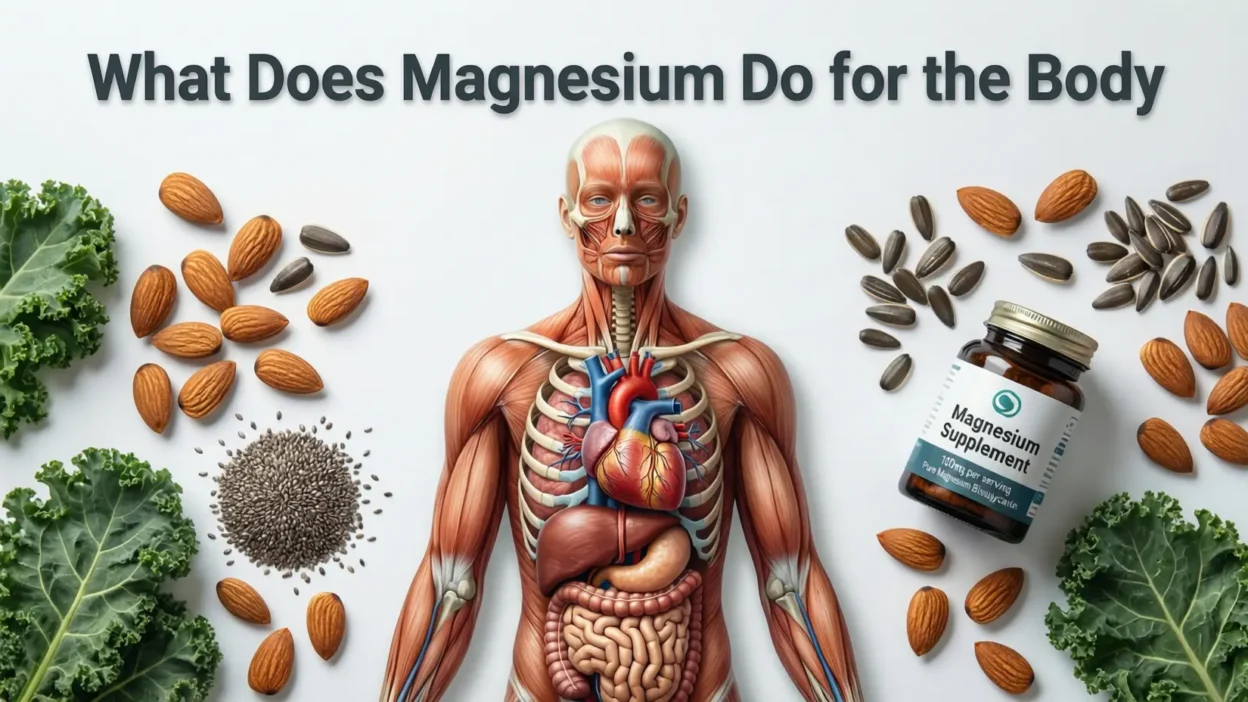
What Does Magnesium Do for the Body?
Magnesium is a vital mineral involved in more than 300 biochemical reactions in the human body.
Your body cannot make magnesium on its own, so you must get it from food or supplements.
At its core, magnesium helps:
- Convert food into energy
- Regulate muscle and nerve function
- Maintain a steady heartbeat
- Support healthy bones and teeth
- Balance blood sugar levels
- Support brain and mood health
Without enough magnesium, many systems in your body begin to struggle even if you don’t notice it right away.
In short:
Magnesium = energy + muscle control + nerve support + heart health
Why Magnesium Is Essential for Overall Health
Magnesium works behind the scenes to keep your body stable and balanced. Unlike vitamins that may have one main role, magnesium supports multiple systems at once.
Here’s why it’s essential:
- It helps enzymes do their jobs
- It allows muscles to relax after contracting
- It keeps nerves from becoming overactive
- It helps calcium work properly in bones
When magnesium levels drop, your body may respond with cramps, fatigue, headaches, anxiety, or irregular heartbeat.
Magnesium and Muscle Function
One of magnesium’s most important roles is muscle control.
Magnesium helps muscles:
- Contract properly
- Relax fully after movement
- Prevent cramps and spasms
Low magnesium levels are often linked to:
- Muscle cramps
- Twitching
- Tightness
- Restless legs
That’s why athletes and physically active people often need more magnesium, especially if they sweat a lot.
Magnesium’s Role in Brain and Nerve Health
Your nervous system relies heavily on magnesium to stay calm and balanced.
Magnesium helps:
- Regulate neurotransmitters
- Reduce nerve overstimulation
- Support memory and focus
- Promote relaxation
Low magnesium levels have been linked to:
- Anxiety
- Irritability
- Poor concentration
- Sleep problems
This is why magnesium is often called a “calming mineral.”
How Magnesium Supports Heart Health
Magnesium plays a key role in keeping your heart rhythm steady.
It helps:
- Regulate heartbeat
- Control blood pressure
- Balance potassium and calcium levels
- Support healthy blood vessels
Adequate magnesium intake is associated with a lower risk of high blood pressure and heart disease.
Magnesium and Energy Production
Feeling tired even after resting? Magnesium might be part of the reason.
Magnesium helps convert food into ATP, the molecule your body uses for energy. Without enough magnesium:
- Energy production slows
- Fatigue increases
- Physical and mental exhaustion become more common
This is why magnesium deficiency often shows up as chronic tiredness.
Magnesium and Bone Health
While calcium gets most of the attention, magnesium is just as important for strong bones.
Magnesium helps:
- Activate vitamin D
- Regulate calcium absorption
- Maintain bone structure
About 60% of magnesium in the body is stored in bones, making it essential for long-term skeletal health.
Magnesium and Sleep Quality
Magnesium supports better sleep by:
- Activating calming neurotransmitters
- Helping muscles relax
- Reducing stress hormones
Many people take magnesium in the evening to:
- Fall asleep faster
- Sleep more deeply
- Wake up feeling more refreshed
Signs of Magnesium Deficiency
Magnesium deficiency is more common than many people realize.
Common signs include:
- Muscle cramps or spasms
- Fatigue or weakness
- Headaches or migraines
- Anxiety or irritability
- Poor sleep
- Irregular heartbeat
Long-term deficiency may increase the risk of:
- Heart disease
- Osteoporosis
- Type 2 diabetes
Foods Rich in Magnesium
The best way to get magnesium is through whole foods.
Top magnesium-rich foods include:
- Leafy greens (spinach, kale)
- Nuts (almonds, cashews)
- Seeds (pumpkin seeds, chia seeds)
- Whole grains
- Legumes
- Dark chocolate
A balanced diet usually provides enough magnesium for most people.
Magnesium Supplements: Are They Necessary?
Some people may benefit from supplements, especially if they:
- Have digestive disorders
- Eat a highly processed diet
- Experience frequent muscle cramps
- Have chronic stress
Common forms include:
- Magnesium citrate
- Magnesium glycinate
- Magnesium oxide
Always follow recommended doses and consult a healthcare professional if unsure.
How Much Magnesium Does the Body Need?
Recommended daily intake varies by age and gender:
- Adult men: ~400–420 mg
- Adult women: ~310–320 mg
Needs may increase during:
- Pregnancy
- Intense physical activity
- High stress periods
Can You Take Too Much Magnesium?
Too much magnesium from food is rare. However, excessive supplementation may cause:
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Stomach cramps
Stick to recommended doses unless advised otherwise by a professional.
FAQs About Magnesium
Is magnesium good for stress?
Yes, magnesium helps calm the nervous system and reduce stress responses.
Does magnesium help with sleep?
Yes, it supports relaxation and may improve sleep quality.
Can magnesium reduce muscle cramps?
Yes, especially cramps caused by deficiency or overuse.
Is magnesium safe daily?
Yes, when taken within recommended amounts.
Does magnesium help brain function?
Yes, it supports memory, focus, and nerve communication.
Conclusion
Magnesium may not get as much attention as other nutrients, but its impact on the body is enormous. From keeping muscles relaxed and nerves calm to supporting heart rhythm, bone strength, energy production, and sleep quality, magnesium is truly a multitasking mineral.
Many common health complaints—fatigue, cramps, anxiety, poor sleep—can be linked to low magnesium levels without people realizing it. By eating magnesium-rich foods and paying attention to your body’s signals, you can support better health naturally.
A small mineral can make a big difference when it comes to how your body feels and functions every day.

I’m Elijah, the mind behind Punsboxx.com. As a true Pun Master, I love twisting words into clever laughs and serving fresh humor that never goes out of style!